https://github.com/takagi/cl-voxelize.git
git clone 'https://github.com/takagi/cl-voxelize.git'
(ql:quickload :cl-voxelize)
Cl-voxelize is a library to convert polygon models into voxel models for particle-based physics simulation.
Here shows an example of how to use cl-voxelize. With the Stanford bunny's ply file, I illustrate how to load, voxelize and visualize it.
As an example data, use the Stanford bunny's ply file from the Stanford 3D Scanning Repository. Since the voxelization algorithm I adopt does not work well for polygon model with holes, I use Stanfords's Volfill tool for hole filling. Additionally, I simplify the model with QSlim for reducing voxelization time. This simplification make no effect on the result voxels in this case, because relatively coarse resolution is enough for particle-based simulation. A hole-filled and simplified Stanford bunny's ply file is placed in this repository.
A hole-filled and simplified Stanford bunny in PLY format: * https://github.com/takagi/cl-voxelize/blob/master/examples/bunny.ply
Read the Stanford bunny's .ply file and convert it to a list of triangles which is input to voxelize function.
(defun triangles (vertices faces)
;; make a list of triangles from vertex array and face array
(let (ret)
(dotimes (i (array-dimension faces 0))
(let ((face (aref faces i)))
(let ((v0 (aref vertices (nth face 0)))
(v1 (aref vertices (nth face 1)))
(v2 (aref vertices (nth face 2))))
(push (list v0 v1 v2) ret))))
ret))
(defun ply-to-triangles (path)
(cl-ply:with-ply-for-reading (plyfile path)
(let ((vertices (make-array (cl-ply:ply-element-size plyfile "vertex")))
(faces (make-array (cl-ply:ply-element-size plyfile "face"))))
;; read vertices
(loop repeat (array-dimension vertices 0)
for i from 0
do (setf (aref vertices i)
(cl-ply:ply-read-element plyfile "vertex")))
;; read faces
(loop repeat (array-dimension faces 0)
for i from 0
do (setf (aref faces i)
(car (cl-ply:ply-read-element plyfile "face"))))
;; get triangles from vertices and faces
(triangles vertices faces))))
Voxelize the obtained triangles and get voxels as the result. The voxels are represented as a list of their center points.
(let ((triangles (ply-to-triangles "/path/to/bunny.ply"))
(delta 0.0045))
(voxelize triangles delta))
As an illustration, I show you the result voxels rendered with POV-Ray.
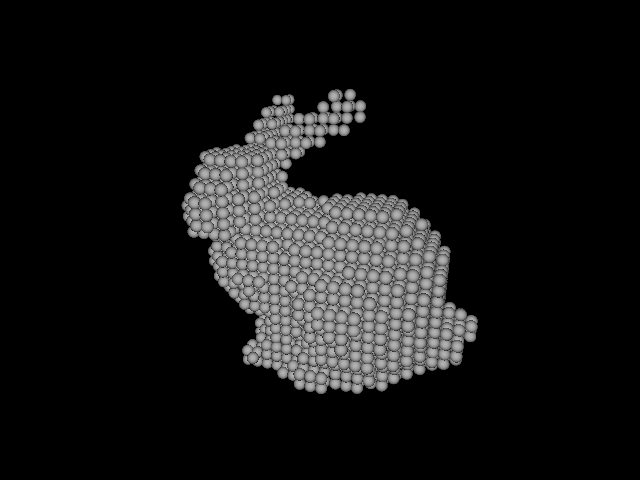
You can install cl-voxelize via Quicklisp:
(ql:quickload :cl-voxelize)
VOXELIZE triangles delta &optional antialias-p => voxels
Returns voxels with given triangles which is a list of triangles. delta is a floating point which specifies the resolution of voxels. voxels is represented as a list of voxels' center points. If antialias-p is true, the result is antialiased.
DO-VOXELIZE ((x y z) triangles delta &optional antialias-p) &body body => result
do-voxelize is a voxelize's counterpart in do- style. Voxels' center points are bound to x, y and z symbols.
Q. What are file formats to be voxelized?
A. Any file formats are supported as far as they can be converted to fit cl-voxelize's API interface.
Q. How large polygon model? How long does it take to voxelize?
A. Currently I do not set performance goal because relatively coarse resolution is enough for particle-based simulation.
Q. Are there any restrictions for polygon models to be voxelized?
A. The voxelization algorithm I adopt does not work well for polygon models with holes.
Q. In a quadtree used in this implementation, how is a triangle which intersects with multiple sub-quadtrees treated?
A. There are roughly two options how to treat a triangle which intersects with multiple sub-quadtrees: * A triangle belongs to all sub-quadtrees with which it intersects * A triangle belongs to only one of sub-quadtrees with which it intersects
To properly determine inside/outside in this case, I choose the former.
Q. If a ray goes on a shared side of triangles through, is inside/outside rightly determined?
A. To determine inside/outside in such case, duplicated intersections are removed.
Q. What are tools used to make the Stanford bunny's ply file in Example section?
A. Tools I used were following: * ply2vri - a simple command line tool for converting triangle meshes in PLY format into signed-distance volumetric grids in VRI format * Volfill - a program for filling in holes in dense polygon meshes using an algorithm based on volumetric diffusion * VRIP - to convert a VRI file to a new triangle mesh in PLY format using the embedding implementation of Marching Cubes * QSlim - a program to simplify polygon model with QEM(Quadratic Error Metric) * Blender - just for converting PLY format from/to OBJ format to apply QSlim
Copyright (c) 2014 Masayuki Takagi (kamonama@gmail.com)
Licensed under the LLGPL License.